
(2010) Diagnosis and management of iron deficiency anaemia: a clinical update. Iron is an important mineral that is involved in red blood cell metabolism and oxygen transport. World J Gastroenterol 16(22): 2720–2725.Ĥ)Pasricha SR, Flecknoe-Brown SC, Allen KJ, Gibson PR, McMahon LP, Olynyk JK, Roger SD, Savoia HF, Tampi R, Thomson AR, Wood EM, Robinson KL. (2010) Treatment of iron deficiency anemia associated with gastrointestinal tract diseases. (2015) Intravenous Iron Therapy in Patients with Iron Deficiency Anemia: Dosing Considerations. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 100(7):301-3.Ģ) Koch TA, Myers J, Goodnough LT. (1970) Intravenous iron-dextran: therapeutic and experimental possibilities. Since this is less than the threshold of total dose of 20 mg/kg, the deficit can be eliminated with a single infusion.ġ) Ganzoni AM. Iron studies are used to identify iron deficiency or. Taking the case of a patient weighing 75 kg (165.3 lbs) with a target hemoglobin value of 13 g/dL (130 g/L or 8.07 mmol/L), an actual hemoglobin of 9.5 g/dL (95 g/L or 5.9 mmol/L) and iron stores of 500 mg, the iron deficit is: Iron is an important mineral that is involved in red blood cell metabolism and oxygen transport. The therapeutic management of IDA focuses on the replenishment of the iron stores through methods that have been mentioned above.
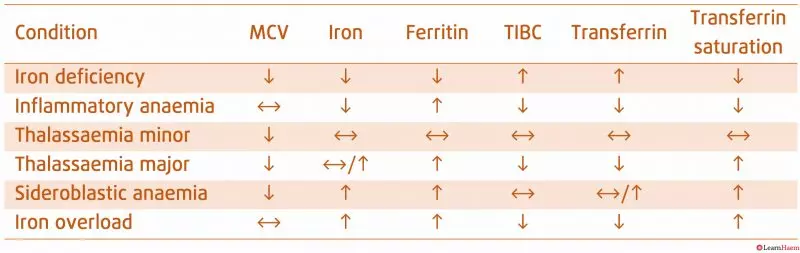
Iron studies interpretation full#
IDA diagnosis is based on full blood examination and on the serum ferritin level. Fulminant symptoms include confusion, sensation of passing out, paleness. IDA symptoms vary, may not be specific and include tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath.
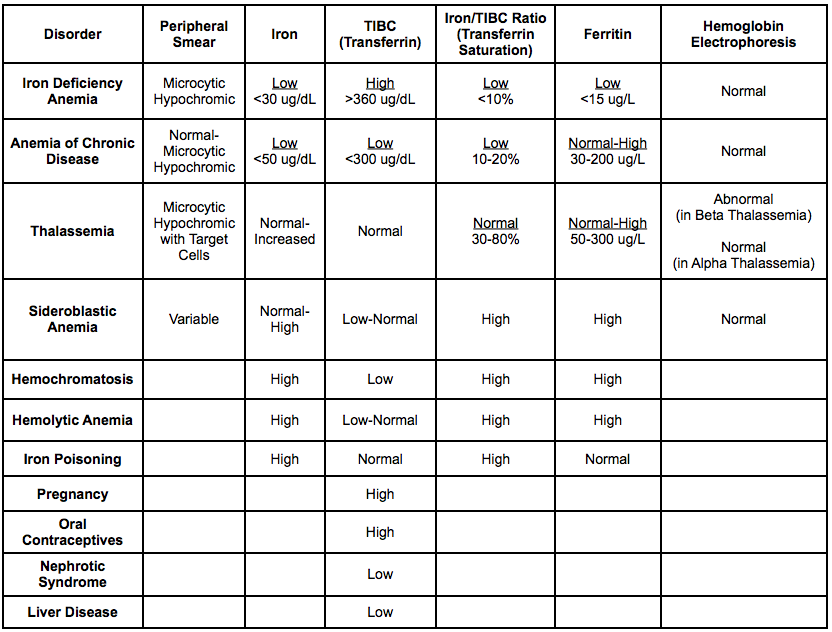
Iron metabolism needs to be balanced and bleeding, the major cause of iron deficiency (for instance in menstruation in females and chronic occult gastrointestinal bleeding) needs to be addressed.Īnemia caused by the depletion of iron is called iron deficiency anemia. Iron deficiency can occur at any stage of life, due to physiological demands, for example, during pregnancy, childhood growth or prolonged periods of sickness. Intravenous therapy is usually recommended in case of contraindications to oral iron, comorbidities that prevent absorption, chronic renal impairment or iron replacement needs to be rapid. Iron supplements, regardless of their way of administration, are used to replete body stores and to correct anemia. It varies from increases in dietary intake of iron (usually for prophylaxis purposes) to oral, intramuscular or intravenous therapy. The iron formulation choice remains for the clinician to make. This may be due to haemochromatosis, or one of several secondary causes of iron overload. Iron Overload This refers to an excess of total body iron stores. If a soluble transferrin receptor is ordered, this is usually increased. Iron replenishment can be done intravenously, either as total dose (example: iron-dextran or iron – carboxymaltose) or as split dose (example: iron sucrose). Iron studies reveal a reduced ferritin level and reduced transferrin saturation. The recommendation is that most adults need a cumulative dose of elemental iron of at least 1 g.

Total iron deficit (mg) = Weight in kg x (Target Hb - Actual Hb in g/dL) x 2.4 + Iron stores The Ganzoni equation used by the iron deficiency calculator is the following: ■ Iron stores – 500 mg for body weight greater than or equal to 35 kg (77 lbs) and 15 mg/kg for body weight less than 35 kg. These can be input in g/dL, g/L or mmol/L. ■ Hemoglobin – there are two fields for hemoglobin input, one for the target and another for actual value. The original formula employs the weight in kg but users can input it in lbs and it gets transformed. ■ Weight – body weight is used to establish iron deficit and is also taken into account when estimating the iron stores. There are four fields that need to be completed: This health tool computes the iron deficit based on patient parameters and the Ganzoni formula. O symptoms of anaemia-such as lethargy, shortness of breath, palpitations, pallor, headache, atrophic glossitis, angular cheilosis.How does this iron deficiency calculator work? O investigating aetiology of low haemoglobin O later manifestations might include deranged liver enzymes, cirrhosis, erectile dysfunction, arthritis, or cardiomyopathy O at early stages can be asymptomatic or present with vague symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or generalised joint pains Box 1: Suggested indications for iron studies


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
